TAX
Tax is a form of payment issued by the government to raise revenue to pay for public services. The Tax collected from the people are generally used to pay for things such as public hospitals, schools and universities, defense and other important aspects of daily life. There are different types of taxes, mainly:
A direct tax is collected directly from the person by the means of income tax, corporate tax etc. whereas an indirect tax is collected by an intermediary by the means of a retail store or vat.
NEED OF TAX IN UAE
The introduction of tax in UAE is a part of the GCC-wide initiative. The intent of tax is to diversify regional economies in the country. The reduction of oil prices in the recent year and also the dependency on hydrocarbons made the GCC member states to impose revenue-raising measures. The GCC member states have agreed to sign unified framework agreements for the implementation of VAT and Excise taxes.
The UAE government provide many public services like healthcare, roads, education, parks, social services and waste management. The expenses of these services are paid by the government budgets. VAT and Excise taxes will provide our country with a new source of income to continue delivering excellent public services and ensure a high quality of life.
HOW TAX WORKS
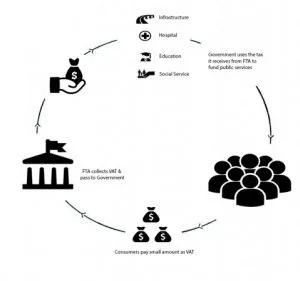
VALUE ADDED TAX
Value-Added Tax or VAT is an indirect tax on the consumption or use of goods and services. VAT is imposed on most supplies of goods and services that are bought and sold. VAT is a form of indirect tax and is used in more than 180 countries around the world.
VAT is charged at each step of day to day expenses. Ultimate consumers generally bear the VAT cost while Businesses collect and account for the tax. Businesses act as a tax collector on behalf of the government.
VAT will be introduced across the UAE on 1 January 2018 at a standard rate of 5%.
The below illustration demonstrates how VAT works throughout a business:
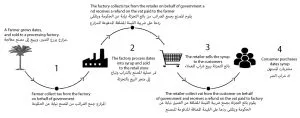
A farmer grows dates which are plucked and sold to a factory for 1000aed. The farmer collects VAT (5%) from the factory on behalf of government (1000 + 50 = 1050aed). The factory processes the dates and makes dates syrup which is sold to a retail shop for 3000aed. The factory collects VAT from the retailer on behalf of the government (3000 + 150 = 3150aed). The factory receives a refund on the vat paid to the farmer (150 – 50 = 100aed). The Date syrups are stocked in stores and placed for sale to consumers for 5000aed. The retail store collects VAT from the consumer on behalf of the government (5000 + 250 = 5250aed). The retailer receives a refund on the VAT paid to the factory (250 – 150 = 100aed).
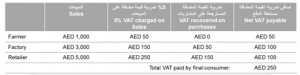
In UAE, VAT will be of 5% on most goods and services, although there will be some exceptions. Consumers generally pay VAT in the form of a 5% increase in most goods and services they purchase in UAE.
VAT will be charged at 0% for the following main categories:
The following categories of supplies will be exempt from VAT:
EXCISE TAX
Excise Tax is a form of indirect tax on specific goods that are harmful to human health or the environment. The intent of excise tax is to reduce the use of harmful commodities.
The following goods will be applicable to excise tax:
The consumer needs to pay a higher retail price once Excise Tax is implemented. The rates to be applied in the UAE will be:
VAT FOR BUSINESS

